
SCIENTIFIC NOTATION
DEFINITION The expressing of a very large or very small number in power of ten is known as scientific notation
DEFINITION
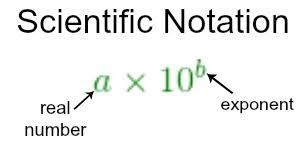
The product of co-efficient 'M' and power 10 'P' is called scientific notation

EXPLANATION
In Physics we deal with a very large or very small numbers. Therefore ,to save time and space we convert the number to standard form. There must be only one-zero digit to the left of a decimal point while writing number in standard form. The power of ten is positive for large numbers while negative for small numbers
STEPS FOR CONVERSION TO SCIENTIFIC NOTATION
STEP 1 :
Locate the position of decimal point
STEP 2 :
Move the decimal point and place it after first non-zero digit
STEP 3 :
If the decimal is moved towards left from its initial position then the power of 10 will be positive and the value of power of 10 will be the number of digit through which the decimal point has been moved
STEP 4
If the decimal is moved towards right from its initial position then power will be negative and the value of power of 10 will be the number of digit through which the decimal point has been moved
EXAMPLE
*) Average distance between earth and moon is 384,400,000 m. For standard form we can write it as
distance = 384,400,000×10^0 m
distance = 3.84400000×10^8 m.
distance =3.844×10^8 m























